Energy IQ: Twenty energy terms described in 50 words or less
You have questions about energy, we have answers. In our latest Energy IQ article, we take a stab at defining 20 energy-related terms in 50 words or less.
By Aytek Yuksel, Content Marketing Leader - Power Systems

Energy is the cornerstone of our lives. We often use six different forms of energy within the first hour of our day. Washing your face requires electric energy to be converted to kinetic energy within the water pump. Using the stove to cook breakfast converts the chemical energy within natural gas to heat (thermal energy). Turning on the TV converts electric energy to light and sound, two more forms of energy.
In our latest Energy IQ article, we've attempted to describe 20 common energy terms in 50 words or less. You might be aware of some of these, yet some might be relatively new for you.
Let's start with the basics. Here are three key words that are used quite frequently: Energy, electricity and power.
What is energy?
Energy is the capacity of doing work. Energy can't be created or destroyed, but only converted from one form to another, according to the first law of thermodynamics. There are nine forms of energy, and we convert energy between these forms to get the needed work done.

What is power?
Power is the time rate of performing the work. As you apply power (watts) over time (hours), energy is consumed (watt-hours). Many devices generate power; a diesel electric generator produces power by converting chemical energy to electricity, and a solar panel produces power by converting the energy of sunlight into electricity.
What is electricity?
Electricity is simply one of the many forms of energy and is created by the movement of electrons. The ease of distribution and the ability to use it safely makes electricity a popular form of energy in our lives.
The simple experiment outlined in this article will help you never forget the difference between power and energy, and details the differences between energy, electricity and power.
Many technologies and components work together to bring us the energy, power and electricity we need. Let's start with the system level terminology before covering individual components.
What is distributed generation?
Distributed generation is an interconnected ecosystem of smaller power generation systems at or close to the point of consumption. This proximity reduces the cost, complexity and inefficiency associated with electricity distribution. Distributed generation also offers the benefit of reduced emissions through the integration of renewable sources with existing energy assets.
What is a microgrid?
A microgrid is a local energy system capable of producing, (potentially storing) and distributing energy to the facilities within the network. Microgrids can include several different assets, also called distributed energy resources (DERs). You can read how microgrids work, why we need microgrids and their advantages in this article.
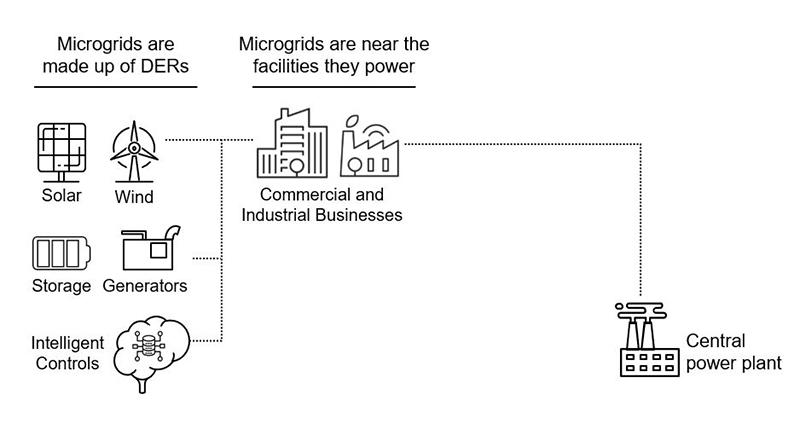
What are distributed energy resources (DERs)?
Distributed energy resources (DERs) are electricity-producing resources connected to the local electric distribution system. Solar photovoltaics (PV), power generators, fuel cells and stationary energy storage systems are some of DER examples. You can read more about three common use cases and deployments of distributed energy resources in this article.
What is a smart grid?
Smart grid refers to modern electric grids where a mix of technologies that enable two-way communication between the utility and its customers. Controls, computing equipment and other digital technologies work together as components of the smart grid to increase the reliability and efficiency of the electric grid.
Let’s now move into individual components that work together within the broader energy eco-system.
What is a power generator?
In electricity generation, a power generator is the device that converts mechanical, chemical, solar or other forms of energy to electricity. The electricity then can be used to power buildings, facilities, homes or mobile applications such as recreational vehicles.
What is a fuel cell?
Fuel cells are energy converters; they convert energy from one form to another. More specifically, fuel cells convert the chemical energy stored in the fuel to electric and thermal energy (heat), without the need for combustion. You can read more about fuel cell basics in this article.
What is a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC)?
A solid oxide fuel cell is a type of fuel cell; it produces electricity, water, heat and small amounts of carbon dioxide. SOFCs can operate at high temperatures, so the system can cope with hydrogen reformer and use natural gas as the fuel. You can read how solid oxide fuel cells work and their advantages in this article.
What is an energy storage system?
Stationary energy storage systems store energy and release it in the form of electricity when needed. An energy storage system usually includes batteries, a control system, inverter and thermal management system in an enclosure. You can read how energy storage systems work and advantages of energy storage systems in this article.
What is an automatic transfer switch (ATS)?
Automatic transfer switches (ATS) switch electrical loads between available power sources. Most often, ATS are used to transfer the electrical load from the utility source to a back-up power generator during a utility power outage. ATS reconnect the load to utility power when the utility power is restored.
Often, electricity generation is simultaneous with the generation of other forms of energy. This simultaneous operation reduces wasted energy and increases energy efficiency. Let's cover the terminology associated with these energy efficient applications.
What is cogeneration, also known as combined heat and power (CHP)?
Cogeneration is the simultaneous production of multiple forms of energy from a single fuel source. Thermal (heat) and electrical (electricity) energy are usually the two forms of energy produced in many types of cogeneration applications. You can read more about how cogeneration works and the advantages of cogeneration in this article.
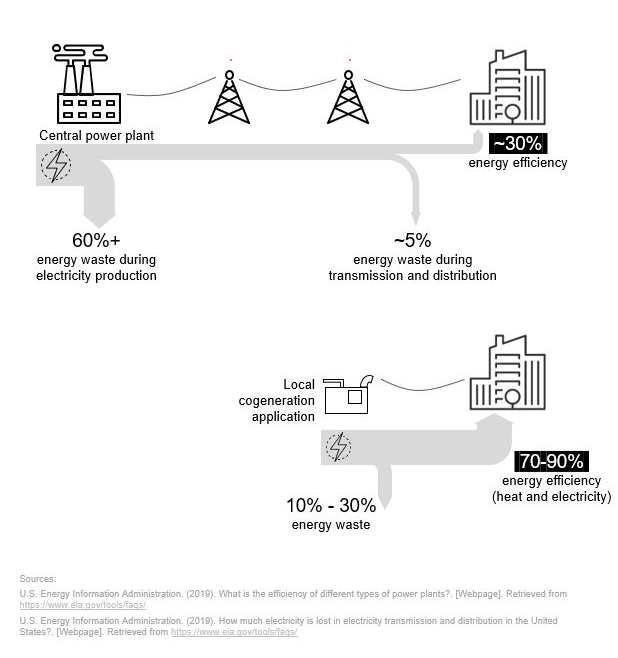
What is trigeneration, also known as combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP)?
Trigeneration is usually the simultaneous production of cooling, heat and electricity through a single fuel source. Some trigeneration applications produce electricity and recover heat while simultaneously utilizing the carbon dioxide (CO2) from the exhaust. This CO2 helps with photosynthesis in greenhouses or carbonation of beverages in bottling facilities.
Let’s now move into the terminology associated with the economic aspects of energy and electricity.
What is spark spread?
The spark spread is a metric for estimating the profitability of natural gas-fired electric generators. It is the difference between the price of electricity and the cost of the natural gas needed to produce that electricity 1. As the spark spread increases, savings provided by a cogeneration system also increases.
What is demand response?
Demand Response is the act of reducing electricity usage during peak demand times to lower your cost of electricity. Generally, customers participate in programs with utilities and agree to reduce demand when needed. To reduce the demand, customers can turn things off, selectively use large loads during off-peak times, or generate their own electricity during peaks.
What is demand charge management?
This is like demand response with a specific focus on reducing demand charges (kW) and associated costs. Demand charge management defines an overall plan which can incorporate several methods of demand reduction and self-generation with the goal of reducing the cost of electricity associated with demand charges (kW).
You can read more about customers' emerging needs around economics, including demand response and demand charge management, making distributed generation an important component of electricity markets in this article.
Let’s wrap by covering the terminology associated with different types of fuels used.
What are renewable energy sources?
Energy sources that naturally replenish over time are called renewable energy sources. Solar, wind, tides, hydropower and geothermal heat are some of the examples for renewable energy sources. While the availability of these renewable energy sources could be intermittent, they are considered inexhaustible over time.
What is diesel fuel?
Diesel fuel is a liquid fuel obtained through distillation of crude oil. Diesel fuel is a mixture of hydrocarbons, aromatics and paraffins with high chemical energy density. An internal combustion engine fueled with diesel converts this chemical energy to heat and kinetic energy.
What is natural gas?
Natural gas is a fuel that primarily consists of methane (CH4); it is colorless and odorless in its original form. Natural gas can be combusted very efficiently and emits less pollutants than many fossil fuels. It has surpassed oil and nuclear to become the second most commonly used fuel in electricity generation.
Sign up below for Energy IQ to receive energy focused insights in markets ranging from data centers and healthcare facilities to schools and manufacturing facilities, and everything beyond. To learn more about the energy and power generation solutions Cummins Inc. offers, visit our webpage.
References:
1 U.S. Energy Administration Office (February 2013). An Introduction to Spark Spreads. Retrieved from https://www.eia.gov/
Author Profiles

Aytek Yuksel, Content Marketing Leader - Power Systems
Aytek is a marketing leader at Cummins, focusing on technology and thought leadership. Since joining in 2008, he has held various marketing roles and now shares insights on markets, technologies, and energy transition. Aytek lives in Minneapolis with his wife and two kids.
Related Tags